Modular vs Manufactured Homes: The Key Differences

In the world of affordable housing, modular homes and manufactured homes provide alternatives to traditional site-built homes. But what sets them apart? In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between modular and manufactured homes to help you make an informed decision.
Modular homes are constructed in line with local, state, and regional building codes, giving them a level of quality assurance. On the other hand, manufactured homes adhere to a federal code set by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). This fundamental difference plays a significant role in terms of regulations, financing options, and long-term value.
Modular homes are built on a permanent foundation and can appreciate in value similar to site-built homes. They offer more customization options and can be financed through a regular mortgage. In contrast, manufactured homes, often referred to as mobile homes, are built on a steel chassis and can be transported from one location to another. They are built to federal safety standards set by the HUD code but may depreciate in value over time. Financing options for manufactured homes are more limited, and they are typically considered personal property rather than real estate.
Key Takeaways:
- Modular homes are held to local building codes, while manufactured homes adhere to a federal code set by the HUD.
- Modular homes can appreciate in value and offer more customization options.
- Manufactured homes are portable and have limited financing options.
- Modular homes are placed on a permanent foundation, while manufactured homes are built on a steel chassis.
- Modular homes can be financed through a regular mortgage, while manufactured homes are often considered personal property.
Now that you have an overview of the key differences, let’s delve deeper into the specifics of modular and manufactured homes to help you decide which option suits your needs and preferences.
What is a Modular Home?
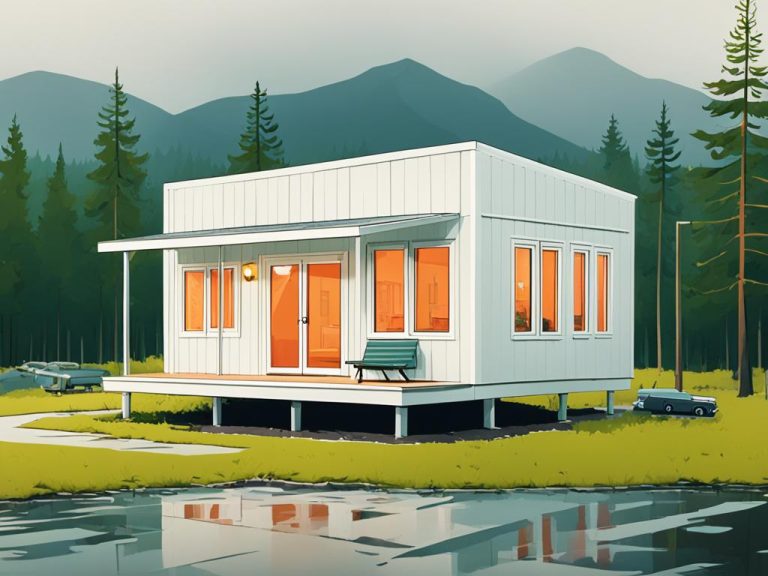
A modular home is a prefabricated home that is partially constructed in a factory and then transported to the homeowner’s lot to be placed on a permanent foundation. Unlike manufactured homes, which are built to federal standards, modular homes are constructed to comply with local building codes and standards. This ensures that they meet the same quality and safety requirements as traditional site-built homes.
Modular homes offer a variety of shapes and sizes, allowing homeowners to choose a layout that suits their needs. They can be customized with different finishes, fixtures, and features, offering a high level of personalization. From the exterior design to the interior layout, homeowners have the freedom to customise their modular homes to reflect their individual style.

One of the major advantages of modular homes is the financing options available. Just like traditional site-built homes, modular homes can be financed through regular mortgages provided by banks and financial institutions. This means that homeowners have access to the same financing opportunities and can benefit from competitive interest rates and terms.
When it comes to the construction process, modules of the modular home are built in a factory setting. Skilled craftsmen construct each module, ensuring precision and quality control. Once the modules are completed, they are transported to the homeowner’s site and assembled on a foundation. This streamlined construction process often results in faster build times compared to traditional site-built homes.
Overall, modular homes offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for homeowners who want a custom-built home with the same financing options as traditional site-built homes. With their ability to meet local building codes, customization options, and faster construction process, modular homes have become an increasingly popular choice in the housing market. Whether it’s a small family home or a spacious retreat, modular homes provide a versatile and personalised living space.
What is a Manufactured Home?
A manufactured home, also known as a mobile home, is a prefabricated home that is built in a factory and transported to the home site in one or multiple sections. These homes are constructed to federal standards set by the HUD code, ensuring quality, durability, safety, fire resistance, energy efficiency, and affordability. Manufactured homes can come in single-wide, double-wide, or triple-wide floor plans, offering a range of sizes and layouts to suit different needs.
Unlike modular homes that are placed on a permanent foundation, manufactured homes can be placed on either a temporary or permanent foundation. They can also be affixed to land, providing homeowners the option to make them a part of their property. This versatility allows for greater flexibility in terms of where the home can be located.
Financing options for manufactured homes may include FHA Title 1 loans, chattel loans, or traditional mortgages if the home is titled as real property. These options provide homeowners with different avenues to secure funding for their manufactured homes based on their individual circumstances and financial preferences.
In conclusion, manufactured homes offer a convenient and affordable housing solution that is built to federal standards with an emphasis on quality and safety. With a variety of floor plans and financing options available, homeowners have the opportunity to own a customized, comfortable, and permanent residence.

Pros and Cons of Modular Homes
Modular homes offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for homeowners. Firstly, modular homes have a shorter construction time compared to site-built homes. This is because the majority of the construction process takes place in a factory, where weather delays are eliminated, resulting in faster completion times.
Another advantage of modular homes is the flexible customization options they provide. Homeowners have the freedom to select different modules that suit their preferences and needs, allowing for a personalized home design. This level of customization is not often available with traditional site-built homes.
Additionally, modular homes contribute to reduced waste during construction. The controlled factory environment enables efficient use of materials, minimizing the amount of waste generated. This not only benefits the environment but also helps to keep costs down.

Furthermore, modular homes have the potential to appreciate in value similar to site-built homes. This means that homeowners can expect their investment in a modular home to grow over time, providing financial stability and potential wealth accumulation.
However, there are some disadvantages to consider when it comes to modular homes. One limitation is the range of available modules, which may restrict the level of customization. Homeowners must work within these limitations to create their desired home design.
Moreover, additional costs may be incurred for utilities and foundation. While the modular home itself may be cost-effective, homeowners need to budget for additional expenses related to connecting utilities and constructing a foundation.
Lastly, some people may hold prejudices about the construction quality of modular homes. However, it’s important to note that modular homes adhere to the same building codes and standards as site-built homes, ensuring structural integrity and safety.
Pros and Cons of Manufactured Homes
Manufactured homes, also known as mobile homes, offer several advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional new homes. Here are some key points to consider:
Advantages of Manufactured Homes
- Affordability: Manufactured homes are generally more affordable than site-built homes, making homeownership more accessible to a wider range of people.
- Faster construction time: Manufactured homes are built in a controlled factory environment, which allows for efficient production and faster construction compared to traditional homes.
- Easy maintenance: The materials and construction methods used in manufactured homes often require less maintenance, making them convenient for homeowners with busy lifestyles.
- Warranty options: Many manufactured homes come with warranties, providing homeowners with peace of mind and protection against potential issues.

Disadvantages of Manufactured Homes
- Equity building: Manufactured homes may not appreciate in value as effectively as site-built or modular homes. This can limit the potential for equity building and long-term financial benefits.
- Limited financing options: Financing options for manufactured homes are more limited compared to traditional homes. This can make it more challenging for some buyers to secure loans with favorable terms.
- Personalization limitations: While some customization options are available, manufactured homes generally offer fewer personalization options compared to site-built or modular homes.
- Location restrictions: There may be restrictions on where manufactured homes can be located, limiting the flexibility of homeowners to choose their desired neighborhood or community.
Considering these pros and cons will help you make an informed decision when considering a manufactured home as a housing option. It’s essential to weigh the advantages of affordability and faster construction against the potential disadvantages of limited financing options and appreciation potential.
Conclusion
When considering modular vs manufactured homes, it’s crucial to evaluate various factors such as cost, customization options, financing choices, construction standards, durability, and long-term value. Modular homes offer greater flexibility in customization and have the potential for appreciating in value, similar to site-built homes. On the other hand, manufactured homes provide an affordable and quicker construction option.
Ultimately, the choice between modular and manufactured homes depends on individual preferences and needs. Those seeking a personalized living space with the ability to appreciate in value may lean towards modular homes. Conversely, individuals looking for cost-effectiveness and faster construction might find manufactured homes more attractive.
Before making a decision, it is advisable to thoroughly research and consider all these factors. Understanding and prioritizing individual requirements will ensure that the chosen home type effectively meets one’s needs and aligns with their budget.
FAQ
What is the difference between modular homes and manufactured homes?
The primary difference between modular homes and manufactured homes is that modular homes are built to local, state, and regional building codes, while manufactured homes are built to a federal code set by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD).
What is a modular home?
A modular home is a prefabricated home that is partially constructed in a factory and then transported to the homeowner’s lot to be placed on a permanent foundation. It must comply with local building codes and standards and offers the same financing options as site-built homes.
What is a manufactured home?
A manufactured home, also known as a mobile home, is a prefabricated home that is built in a factory and transported to the home site. It is built to federal standards set by the HUD code and can come in single-wide, double-wide, or triple-wide floor plans. Financing options may include FHA Title 1 loans, chattel loans, or traditional mortgages.
What are the advantages of modular homes?
Some advantages of modular homes include shorter construction time, flexible customization options, reduced waste during construction, and potential for appreciation in value similar to site-built homes.
What are the advantages of manufactured homes?
Manufactured homes offer affordability compared to traditional new homes, faster construction time, ease of maintenance, and the possibility of coming with warranties.
What are the disadvantages of modular homes?
Disadvantages of modular homes include limitations of customization within the range of available modules, additional costs for utilities and foundation, and potential prejudices about the construction quality.
What are the disadvantages of manufactured homes?
Disadvantages of manufactured homes include limited personalization options, restrictions on where they can be located, limited financing options, and potentially reduced equity compared to site-built or modular homes.
How do I decide between a modular home and a manufactured home?
When deciding between modular and manufactured homes, it’s important to consider factors such as cost, customization options, financing options, construction standards, durability, and long-term value. Modular homes offer more customization and potential for appreciation, while manufactured homes offer affordability and faster construction. Ultimately, the choice depends on individual preferences and needs.





how to buy priligy im 16 years old I celebrated 2 years in remission the week before this event I had 9 tattoos before this and I love that I can point to each one and tell you what was going on in my life when I got it done
Stay informed on world events, policy changes, and sports highlights.
Our dedicated reporters deliver up-to-the-minute updates non-stop.
Ticketmaster
CBD (cannabidiol) like https://www.cornbreadhemp.com/pages/how-long-does-it-take-for-thc-gummies-to-kick-in is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It’s widely habituated to for implied benefits like reducing anxiety, improving take, and relieving torment without the “towering” associated with THC. Handy in oils, gummies, creams, and more, it’s average with a view wellness and remedial uses.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
магазин аккаунтов маркетплейс аккаунтов
аккаунт для рекламы https://marketplace-akkauntov-top.ru/
купить аккаунт покупка аккаунтов
профиль с подписчиками профиль с подписчиками
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей аккаунт для рекламы
заработок на аккаунтах продажа аккаунтов соцсетей
продать аккаунт https://pokupka-akkauntov-online.ru
Gaming account marketplace Account exchange
Sell Pre-made Account Verified Accounts for Sale
Account Sale Account market
Verified Accounts for Sale Guaranteed Accounts
Online Account Store Accounts for Sale
Buy Pre-made Account Buy Account
Online Account Store Website for Selling Accounts
Account marketplace Find Accounts for Sale
Account exchange Purchase Ready-Made Accounts
Accounts market Account Selling Platform
guaranteed accounts secure account sales
account sale online account store
verified accounts for sale database of accounts for sale
marketplace for ready-made accounts marketplace for ready-made accounts
guaranteed accounts purchase ready-made accounts
sell account buy pre-made account
website for buying accounts account acquisition
account trading platform account catalog
account exchange gaming account marketplace
account purchase account store
buy account accounts-marketplace.org
account catalog database of accounts for sale
sell accounts secure account purchasing platform
account market account store
account catalog accounts-for-sale.org
marketplace for ready-made accounts account market
account selling platform guaranteed accounts
account buying service website for selling accounts
account purchase find accounts for sale
account market buy accounts
secure account sales account marketplace
sell accounts account store
account market secure account sales
account buying platform website for selling accounts
account market guaranteed accounts
accounts for sale account market
profitable account sales online account store
account store guaranteed accounts